
Luo S, Peng J, Kunpeng L et al (2011) Contrasting evolutionary patterns of the Rp1 resistance gene family in different species of poaceae.Knox AK, Dhillon T, Cheng H et al (2010) CBF gene copy number variation at Frost Resistance-2 is associated with levels of freezing tolerance in temperate-climate cereals.Bartlett JG, Alves SC, Smedley M et al (2008) High-throughput Agrobacterium-mediated barley transformation.Casu RE, Selivanova A, Perroux JM (2012) High-throughput assessment of transgene copy number in sugarcane using real-time quantitative PCR.Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by Gel-electrophoresis.Southern blotting: a laboratory technique used to detect a specific DNA sequence in a blood or tissue sample. Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size Polymeric: a large/gigantic molecule that is made up of repeating, small molecules called monomers. Nucleotide : a building block molecule of nucleic acids. Southern blotting involves the transfer of DNA to a nylon membrane and probing for the presence of certain sequences.
 Gel electrophoresis depends on the negatively-charged ions present on nucleic acids at neutral or basic pH to separate them based on size. Practice Exam 1 C/P Section Passage 8 Question 41 The electrophoretic separation of proteins Southern blots are used to detect the presence of certain DNA sequences in a given genome, and northern blots are used to detect gene expression. When DNA is transferred to a nylon membrane, the technique is called Southern blotting when RNA is transferred to a nylon membrane, it is called northern blotting. The nucleic acid fragments that are bound to the surface of the membrane can then be probed with specific radioactively- or fluorescently-labelled probe sequences. The fragments in the gel are then transferred onto a nylon membrane in a procedure called blotting. Gel electrophoresis separates the nucleic acid fragments according to their size. Short DNA fragments called probes are designed and labeled with radioactive or fluorescent dyes to aid detection. Nucleic acid samples, such as fragmented genomic DNA and RNA extracts, can be probed for the presence of certain sequences. See the example gel electrophoresis result below. Finally, distinct nucleic acid fragments appear as bands at specific distances from the top of the gel (the negative electrode end) based on their size. Nucleic acids in a gel matrix can be observed using various fluorescent or colored dyes. Researchers use molecular-weight standard DNA samples that can be run alongside the molecules to provide a size comparison and identify the DNA fragment of known size. Smaller molecules move through the pores in the gel faster than larger molecules this difference in the rate of migration separates the fragments based on size. The polymeric gel has porous structures thus acts as a molecular sieve. Samples are loaded into a slot near the negative electrode and pulled toward the positive electrode at the opposite end of the gel.
Gel electrophoresis depends on the negatively-charged ions present on nucleic acids at neutral or basic pH to separate them based on size. Practice Exam 1 C/P Section Passage 8 Question 41 The electrophoretic separation of proteins Southern blots are used to detect the presence of certain DNA sequences in a given genome, and northern blots are used to detect gene expression. When DNA is transferred to a nylon membrane, the technique is called Southern blotting when RNA is transferred to a nylon membrane, it is called northern blotting. The nucleic acid fragments that are bound to the surface of the membrane can then be probed with specific radioactively- or fluorescently-labelled probe sequences. The fragments in the gel are then transferred onto a nylon membrane in a procedure called blotting. Gel electrophoresis separates the nucleic acid fragments according to their size. Short DNA fragments called probes are designed and labeled with radioactive or fluorescent dyes to aid detection. Nucleic acid samples, such as fragmented genomic DNA and RNA extracts, can be probed for the presence of certain sequences. See the example gel electrophoresis result below. Finally, distinct nucleic acid fragments appear as bands at specific distances from the top of the gel (the negative electrode end) based on their size. Nucleic acids in a gel matrix can be observed using various fluorescent or colored dyes. Researchers use molecular-weight standard DNA samples that can be run alongside the molecules to provide a size comparison and identify the DNA fragment of known size. Smaller molecules move through the pores in the gel faster than larger molecules this difference in the rate of migration separates the fragments based on size. The polymeric gel has porous structures thus acts as a molecular sieve. Samples are loaded into a slot near the negative electrode and pulled toward the positive electrode at the opposite end of the gel. 
Because nucleic acids are negatively-charged ions at neutral or basic pH in an aqueous environment, an electric field can mobilize them.
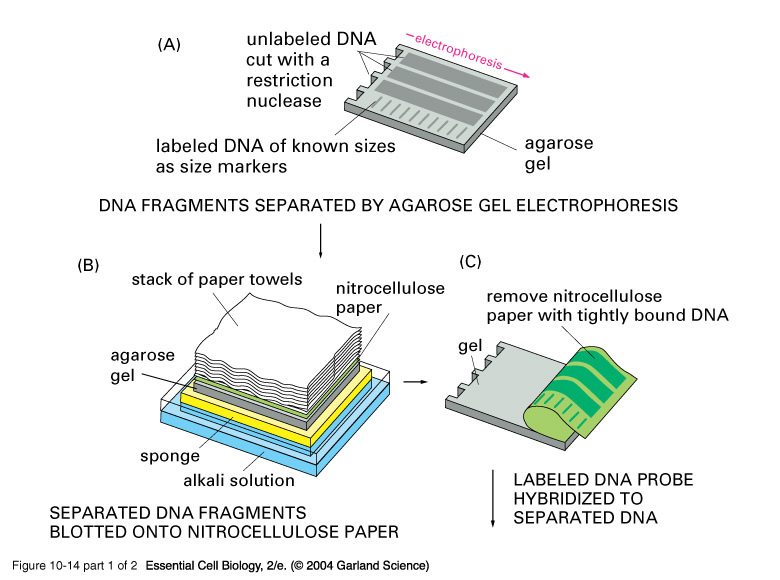
For that, nucleic acid samples are run through a polymeric gel matrix under the electric field. the number of nucleotides) in a sample and visualize them. Gel electrophoresis allows to separate the nucleic acid molecules of various length (i.e. Gel Electrophoresis and Southern blotting are techniques used to characterize DNA samples.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
